Publications
A framework for understanding polyP-chromatin interactions.
PolyPhosphate Condensates, Bacterial Chromatin
Chawla R*, Tom JKA*, Boyd T, Grotjahn DA, Tu NH, Bai T, Park D, Deniz AA†, Racki LR†. Reentrant DNA shells tune polyphosphate condensate size. Nat Commun 15, 9258 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53469-x
Polyphosphate attenuates the motion of GFP-µNS particles in the cytoplasm during nitrogen starvation.
PolyPhosphates, Chromatin, bacterial cell biology, starvation
Magkiriadou S, Stepp WL, Newman DK, Manley S†, Racki LR†. Polyphosphate affects cytoplasmic and chromosomal dynamics in nitrogen-starved Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 9;121(15):e2313004121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313004121. †Corresponding
AlgP, a histone H1-like protein with a c-terminus rich in ‘KPAA’ repeats, localizes to polyphosphate granules and plays a role in their even spacing on the long axis of the cell
PolyPhosphates, Chromatin, bacterial cell biology, starvation
Chawla R*, Klupt S*, Patsalo V, Williamson JR, Racki LR†. The histone H1-like protein AlgP facilitates even spacing of polyphosphate granules in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0246321. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02463-21. †Corresponding
Polyphosphate granules in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell starved 3 hours for nitrogen
PolyPhosphates, bacterial cell biology, starvation
Racki LR, Tocheva EI, Dieterle MG, Sullivan MC, Jensen GJ, Newman DK. Polyphosphate granule biogenesis is temporally and functionally tied to cell cycle exit during starvation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 21;114(12):E2440-E2449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1615575114.
Eukaryotic Chromatin, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling, EPR
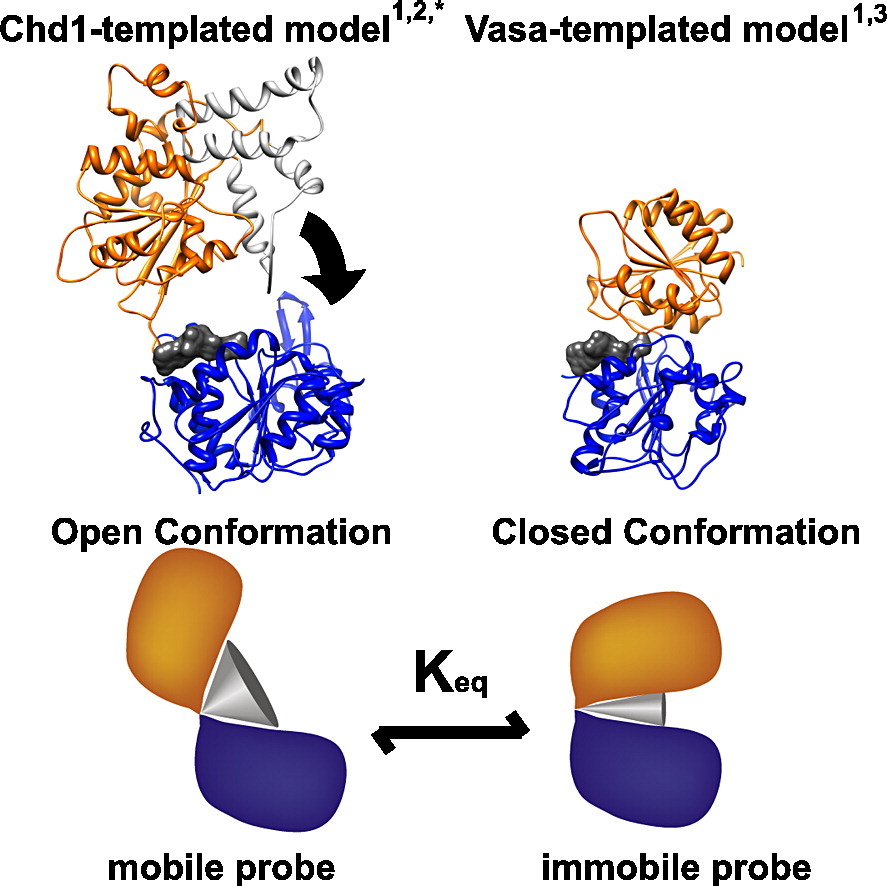
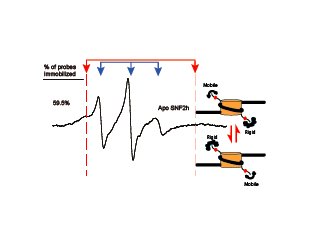
Racki LR*, Naber N*, Pate E, Leonard JD, Cooke R, Narlikar GJ. The histone H4 tail regulates the conformation of the ATP-binding pocket in the SNF2h chromatin remodeling enzyme. J Mol Biol. 2014 May 15;426(10):2034-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Mar 4. PubMed PMID: 24607692; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4059342.pretium massa. *Equal Contribution
Eukaryotic Chromatin, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling
Racki LR*, Yang JG*, Naber N, Partensky PD, Acevedo A, Purcell TJ, Cooke R, Cheng Y, Narlikar GJ. The chromatin remodeller ACF acts as a dimeric motor to space nucleosomes. Nature. 2009 Dec 24;462(7276):1016-21. doi: 10.1038/nature08621. PubMed PMID: 20033039; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2869534. *Equal Contribution
review: Eukaryotic Chromatin, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling
Racki LR, Narlikar GJ. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes: two heads are not better, just different. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008 Apr;18(2):137-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2008.01.007. Epub 2008 Mar 12. Review. PubMed PMID: 18339542; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2494867.
Eukaryotic Chromatin, Post-translational modification
Simon MD, Chu F, Racki LR, de la Cruz CC, Burlingame AL, Panning B, Narlikar GJ, Shokat KM. The site-specific installation of methyl-lysine analogs into recombinant histones. Cell. 2007 Mar 9;128(5):1003-12. PubMed PMID: 17350582; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2932701.